
#NEGATIVE TB TEST RESULTS SKIN#
In the Pirquet version of the test tuberculin is applied to the skin via scarification.

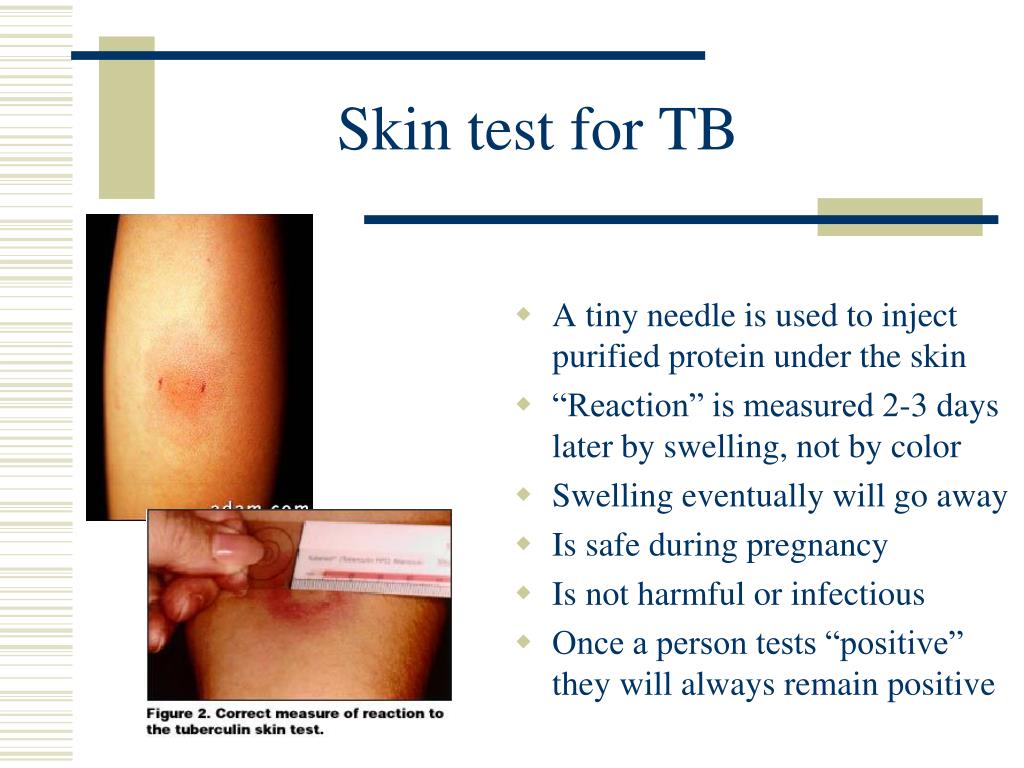
Erythema (redness) should not be measured. If there is no induration, the result should be recorded as "0 mm". The reaction is read by measuring the diameter of induration (palpable raised, hardened area) across the forearm (perpendicular to the long axis) in millimeters. T cells and myeloid cells are attracted to the site of reaction in 1–3 days and generate local inflammation. The response is a classical example of delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction ( DTH), a type IV of hypersensitivities. A person who has been exposed to the bacteria is expected to mount an immune response in the skin containing the bacterial proteins. This intradermal injection is termed the Mantoux technique. The result of the test is read after 48–96 hours but 72 hours (3rd day) is the ideal. When placed correctly, injection should produce a pale wheal of the skin, 6 to 10 mm in diameter. The injection should be made with a tuberculin syringe, with the needle bevel facing upward. In the Mantoux test, a standard dose of 5 tuberculin units (TU - 0.1 ml), according to the CDC, or 2 TU of Statens Serum Institute (SSI) tuberculin RT23 in 0.1 ml solution, according to the National Health Service, is injected intradermally (between the layers of dermis) on the flexor surface of the left forearm, mid-way between elbow and wrist.

In 1954, the Soviet Union started mass production of PPD-L, named after Linnikova. Linnikova created a modified version of PPD. By the 1940s, Seibert's PPD was the international standard for tuberculin tests.

Her first publication on the purification of tuberculin appeared in 1934. Seibert then spent a number of years developing methods for separating and purifying the protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, obtaining purified protein derivative (PPD) and enabling the creation of a reliable test for tuberculosis. Seibert identified the active agent in tuberculin as a protein. However, the test was unreliable due to impurities in tuberculin which tended to cause false results. It is named after Charles Mantoux, a French physician who built on the work of Koch and Clemens von Pirquet to create his test in 1907. The test was first developed and described by the German physician Felix Mendel in 1908. The tuberculin reaction was first described by Robert Koch in 1890. Purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin is a precipitate of species-nonspecific molecules obtained from filtrates of sterilized, concentrated cultures. Tuberculin is a glycerol extract of the tubercle bacillus. Mantoux test injection site in a subject without chronic conditions or in a high-risk group clinically diagnosed as negative at 50 hours It was also used in the USSR and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states, although Soviet mantoux produced many false positives due to children's allergic reaction. The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Heaf test, a form of tine test, was used until 2005 in the UK, when it was replaced by the Mantoux test. It is one of the major tuberculin skin tests used around the world, largely replacing multiple-puncture tests such as the tine test. The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening for tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis diagnosis. The circular shape is known as a wheal response. The Mantoux skin test consists of an intradermal injection of one-tenth of a milliliter (ml) of PPD tuberculin.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
